A brief explanation of crypto art: Blockchain
Read in Indonesian
The crypto art craze has been taken everyone aback lately. Who knew one could sell Nyan Cat Gif for $590,000? Before we dive deeper into NFT, let’s go back to where it begins: the birth of bitcoin.
It was all started in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto - a pseudonym - circulated a PDF file titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System on a mailing list for cryptography. Bitcoin was launched a year later. The first transaction using bitcoin was made in 2010 at a pizzeria. Programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two pizzas from Papa John’s for 10,000 bitcoins.
Bitcoin is one of the most popular cryptocurrencies on the market. Each cryptocurrency has its own blockchain, a system created to support cryptocurrency trading. Blockchain is accessible by anyone with Internet connection.
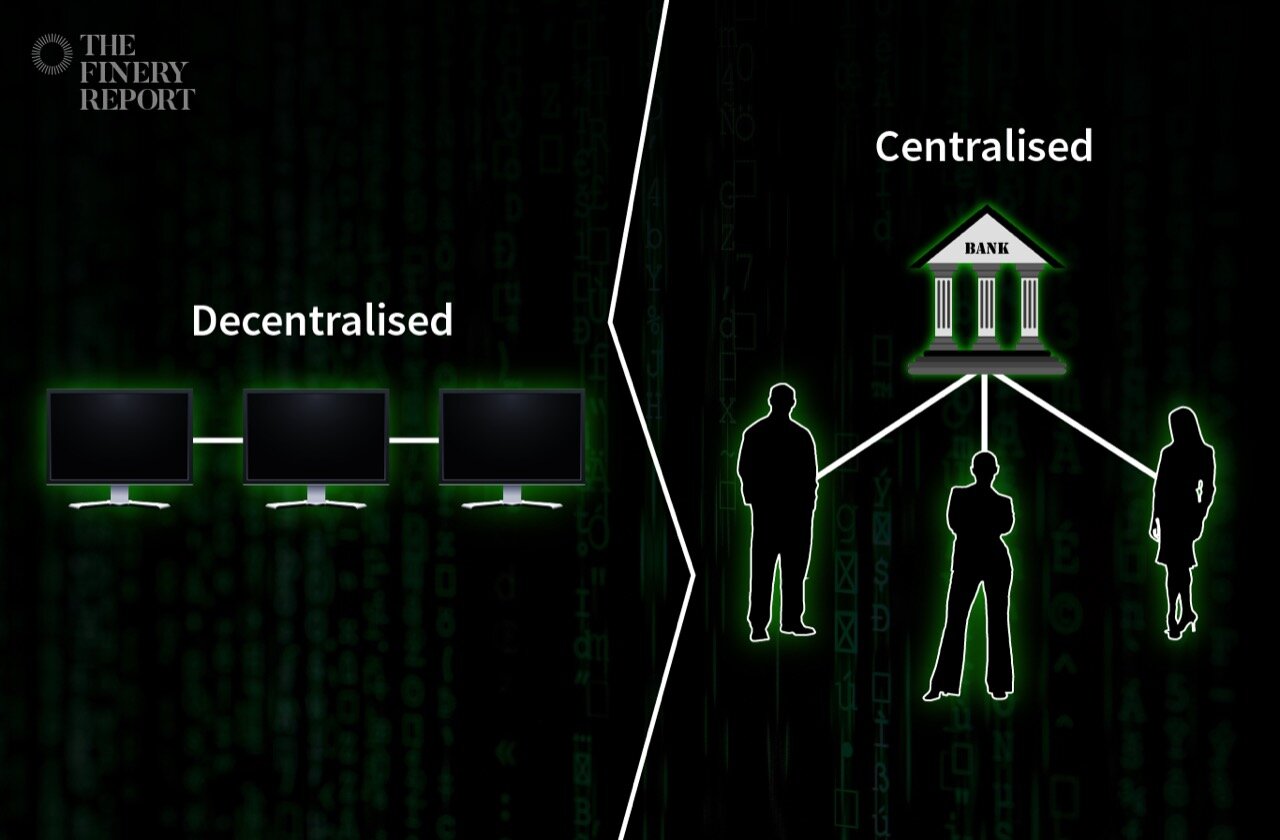
Blockchain consists of sequences of blocks. Each block contains records of every cryptocurrency transaction. Unlike banks, there is no centralised distribution of bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency. It operates with a peer-to-peer network from computers connected to the blockchain.
Let’s use daily activity as an example. When we purchase products at an online store, the store has our purchase history, profile and credit card information. The data is owned by the store only; customers have no access to the information of other customers.
On the other hand, blockchain works as a public ledger where every transaction of cryptocurrency is recorded. Every computer or node connected to a blockchain through the Internet receives the data as well. Nobody owns more or less information than the others who are connected. Everyone receives the same amount of information.
Think of it like a big accounting book where every expense and income are written down. Anyone can access the book and track all the expenses and income recorded in the book from day one, including validating the recorded information.
In a centralised system like banks, the central system do all the validation. For instance, when we use Visa or Mastercard to shop online, only Visa or Mastercard can approve and validate the transaction. In a decentralised system like blockchain, there is no regulator or central authority. All the computers connected to the blockchain can validate the data.
This is also the reason why blockchain is almost impossible to be hacked into. Once recorded, the data of any transaction cannot be altered and erased, let alone tampered.
When hackers hack into a company’s database, they could retrieve or change private information. Only the company knows what has been taken or changed. With blockchain, hackers have to access at least 51% of the computers connected to the blockchain simultaneously in order to successfully tamper with the blocks, something that is impossible to execute since there could be millions of computers connected to a blockchain system.
Getting blockchain and cryptocurrency
What’s interesting about cryptocurrency is that anyone can create their own blockchain and cryptocurrency with coding skills in Java, Javascript, or Python. The success of your own blockchain depends on whether people will adopt it or not. Marketing is necessary in this case.
Besides bitcoin, litecoin and ethereum are also popular cryptocurrencies. There are two methods to get cryptocurrencies, ‘mining’ it or buying it from an exchange platform or website. Both methods require enormous amount of capital, but the latter is simpler. You can purchase cryptocurrency from exchange websites with credit card, bank transfer and cash.
The cryptocurrency will be stored in a cryptocurrency wallet – the same way as we store our money in a bank account. There are online wallets, software wallets and hardware wallets. Hardware wallet is a portable device you can plug into your computer. The choice of wallets depends on the cryptocurrency.
Unlike mining, buying cryptocurrency from exchange websites doesn’t require blockchain. In order to mine a cryptocurrency, you have to install the blockchain of the cryptocurrency you are going to mine. For instance, install bitcoin blockchain if you are going to mine bitcoin.
The process of mining cryptocurrencies is longer and more complex than buying it from an exchange platform. Mining is the process of creating new bitcoin by solving mathematical puzzles or algorithms. In other words, cryptocurrency is a reward for miners. Mining cannot be done on mobile phone or laptop. CPU and mining hardware are necessary. The hardware could cost a fortune and use a huge amount of energy to operate.
Take gold for example. We have the options to purchase the metal in a physical form (coin or bar) directly or invest in gold mutual funds or gold exchange traded funds. Another way to do it is mining the gold, but it requires equipment, expertise, labour, permit and license.
The equipment to mine gold includes excavators, machines and labs, while the equipment to mine cryptocurrency consists of computers, hardware and perhaps, a spacious place to store the hardware.
The more computers or nodes connected to the blockchain and traded cryptocurrency, the more mathematical puzzles or algorithms needed to be solved as the public ledger grows bigger. This is similar to goldmining: the more premises being mined, the scarcer gold becomes.
The only similarity between cryptocurrency and cash is the basic economic theory of supply and demand. Just like banks limiting circulation of banknotes, the supply of bitcoin is limited to 21 million coins. The limit of supply is what drives the high demand and valuation of bitcoin. 18 million coins have been mined so far. The mining of bitcoin is projected to complete by 2140.